Traveller
Traveller is a tiny element which is used in ring spinning system , acts as the main of twist imparter during yarn production. On the other word , it is also called the twisting element merely responsible for twist impartion.It is a C-shaped, metal clip that revolves around the ring on a ring spinning frame. It guides the yarn onto the bobbin as twist is inserted into the yarn.
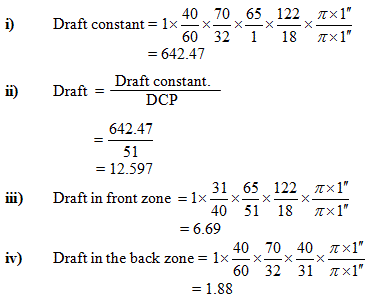
 |
| Ring Traveller |
The traveller allows the twisting and the correct delivery of the yarn on the bobbin. The take up speed of the yarn, which corresponds to the difference between the peripheral speed of the bobbin and the peripheral speed of the traveller, is equal to the peripheral speed of the delivery cylinders of the drafting unit. The difference between spindle rpm and the traveler rpm, within a specific unit of time, gives the number of coils deposited on the bobbin within a specific unit of time. Therefore, with the same spindle speed, the traveller rpm increases along with the bobbin diameter while the number of coils wound on the bobbin decreases.
When the traveller rotates the high contact pressure between the ring and the traveller creates huge friction forces that generate heat; the traveller can reach temperatures exceeding 200 ÷ 300 °C since its small mass does not allow a quick transfer of the heat to the air or to the ring. For this reason, significant improvements in ring spinning can be hardly achieved with the materials currently available, since the speed of the traveller has apparently reached its maximum limit (approx. 33 ÷ 35 m/sec for steel travellers and 45 ÷ 47 m/s for nylon-glass fibre travellers). This is why the traveller used for producing a specific type of yarn must feature the most suitable shape, mass, material, finish and cross section. To reach the highest speeds, the shape of the traveller must correspond to the shape of the ring.
This creates a very large contact surface, which facilitates heat transfer; the surface must also be very smooth to grant a low barycentre. The flat profile must allow space enough for the yarn since the friction between the yarn and the ring could increase the yarn hairiness and consequently the formation of flying fibres.
The mass of the traveller determines the friction force between the ring and the traveller, the balloon size and consequently the take up tension of the yarn. If the mass of the traveller is very small, the balloon will be sufficiently large, the take up tension will be limited and the bobbin will be soft; on the contrary, a heavy traveller will determine an increase in the take up tension and a greater number of breaks. In a few words, the mass of the traveller must be strictly proportional to the yarn mass (count and resistance) and to the speed of the spindle.
When the traveller rotates the high contact pressure between the ring and the traveller creates huge friction forces that generate heat; the traveller can reach temperatures exceeding 200 ÷ 300 °C since its small mass does not allow a quick transfer of the heat to the air or to the ring. For this reason, significant improvements in ring spinning can be hardly achieved with the materials currently available, since the speed of the traveller has apparently reached its maximum limit (approx. 33 ÷ 35 m/sec for steel travellers and 45 ÷ 47 m/s for nylon-glass fibre travellers). This is why the traveller used for producing a specific type of yarn must feature the most suitable shape, mass, material, finish and cross section. To reach the highest speeds, the shape of the traveller must correspond to the shape of the ring.
This creates a very large contact surface, which facilitates heat transfer; the surface must also be very smooth to grant a low barycentre. The flat profile must allow space enough for the yarn since the friction between the yarn and the ring could increase the yarn hairiness and consequently the formation of flying fibres.
The mass of the traveller determines the friction force between the ring and the traveller, the balloon size and consequently the take up tension of the yarn. If the mass of the traveller is very small, the balloon will be sufficiently large, the take up tension will be limited and the bobbin will be soft; on the contrary, a heavy traveller will determine an increase in the take up tension and a greater number of breaks. In a few words, the mass of the traveller must be strictly proportional to the yarn mass (count and resistance) and to the speed of the spindle.
Features of a Traveller:
- Generate less heat
- Dissipate heat fastly
- Have sufficient elasticity for easy insertion and to retain its original shape after insertion
- Friction between ring and traveller should be minimal
- It should have excellent wear resistance for longer life
- Hardness of the traveller should be less than the ring
Traveller are normally three types. They are:
- OS -Type
- C-Type
- G-Type
- Count of yarn to be spun
- Fiber used in the yarn
- Ring cup diameter
- Spindle speed